stem cell transplant, as a highly regarded cutting-edge therapy in modern medicine, has increasingly come into the limelight in recent years. Many people may wonder what diseases can be treated with stem cell transplantation. Why do some people say it is a "lifesaver" for leukemia patients, while others mention that it can be used for autoimmune diseases?
This article will take you through the full range of indications for stem cell transplantation, from hematologic disorders toautoimmune diseaseand then to some rare genetic diseases.Helping you make sense of the applications of stem cell transplantationThe
I. What diseases can stem cell transplantation cure?
1. Hematologic malignancies
Hematologic malignancies are one of the earliest and most mature areas of application for stem cell transplantation. For these diseases, the patient's hematopoietic system is often infested or damaged by abnormal cells, and stem cell transplantation can replace the damaged stem cells and rebuild a healthy blood system, thus improving survival rates.
Common indications include:
-
acute leukemia(e.g. AML, ALL)
-
chronic leukemia(e.g. CML)
-
lymphomas(Hodgkin's lymphoma, non-Hodgkin's lymphoma)
-
myelodysplastic syndrome (medicine)
For these patients, stem cell transplantation not only removes the abnormal cells, but also helps restore hematopoietic function, offering the possibility of long-term recovery.
2.Non-malignant blood diseases
In addition to malignant tumors, stem cell transplantation can also be applied to some non-malignant blood diseases, such as severe anemia or thrombocytopenia. Such diseases, although not cancerous, can lead to reduced immunity, susceptibility to infections or other health problems.
Common indications include:
-
aplastic anemia (med.)
-
Severe anemia or thrombocytopenia
-
Immunocompromised due to blood diseases
Through stem cell transplantation, patients are able to restore their hematopoietic function, reduce their risk of infection, and significantly improve their overall quality of life.
3. Hereditary blood and metabolic disorders: Improvement of body condition from the root
For some hereditary blood or metabolic diseases, traditional medication often only relieves the symptoms, while stem cell transplantation can radically improve the patient's constitution. By replacing or repairing abnormal stem cells, the patient's blood or immune system function is restored.
Typical indications include:
-
Thalassemia (β-thalassemia)
-
sickle cell anemia
-
Certain inborn defective metabolic diseases
For pediatric patients in particular, early stem cell transplantation not only improves survival, but also significantly improves quality of life and provides a better health foundation for future growth.
4. Autoimmune diseases
In recent years, the use of stem cell transplants in autoimmune diseases has received increasing attention. Autoimmune diseases are chronic diseases caused by the immune system attacking its own tissues, and stem cell transplants can "reset" the immune response by rebuilding the immune system, thereby reducing symptoms and even achieving long-term remission.
Common indications include:
-
Systemic Lupus Erythematosus (SLE)
-
Multiple Sclerosis (MS)
-
Severe rheumatoid arthritis (RA)
-
Scleroderma and systemic sclerosis
Typically, this type of treatment is indicated for patients who are not responding well to medication or who have more severe disease. Clinical studies have shown that some patients experience significant improvement in their symptoms and quality of life after transplantation.
5. Congenital immunodeficiency diseases
For patients with congenital immunodeficiency diseases, the immune system is inherently deficient and prone to infections that are difficult to control. Stem cell transplantation can replace the abnormal immune cells and help patients establish normal immune function, thereby significantly improving survival and health.
Typical indications include:
-
Severe Combined Immunodeficiency (SCID)
-
Wiskott-Aldrich syndrome
-
Other rare congenital immunodeficiency diseases
Early stem cell transplantation is especially important to provide long-term health for the child.
6. Certain solid tumors and genetic diseases
Although the application of stem cell transplantation in solid tumors is still in the exploratory stage, it can accelerate bone marrow recovery, reduce the risk of infection, and help the body recover quickly in patients after intense chemotherapy. In addition, studies of some genetic diseases have shown that stem cell transplantation may become an adjunctive treatment, providing new hope for these patients.
Application scenarios include:
-
Bone marrow recovery after high-intensity chemotherapy
-
Adjuvant therapy for selected rare genetic diseases
Although these applications need to be supported by more clinical data, they offer great promise for the future development of stem cell transplantation.
Second, the core principle: why can stem cell transplantation treat these diseases?
Stem cell transplantation works through two main core mechanisms:
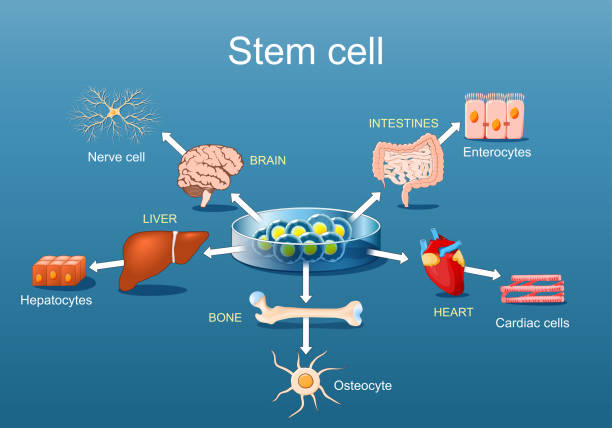
1. Rebuild the hematopoietic and immune systems:This is the most fundamental role. The patient's body is cleared of diseased bone marrow cells (including cancerous immune cells) through high-dose chemotherapy or radiation, and healthy stem cells are then infused back into the body as "seeds". These seeds take root in the bone marrow "soil" and grow a healthy blood and immune system again.
2. Graft-versus-tumor effect (GVT):this isallograftUnique advantage. The transplanted donor immune cells will recognize and attack residual tumor cells in the patient's body, creating a beneficial "immune cleansing" effect that can significantly reduce the recurrence rate of leukemia and other diseases.
III. Contraindications and Risk Tips for Stem Cell Transplantation
It is important to note thatStem cell transplants are not for everyone, it is usually used for patients with more severe disease and limited results from conventional treatment. Suitability for transplantation needs to be assessed by a medical professional for the type of disease, physical condition and donor match.
Overall, as the technology has matured and experience has been gained in its management, the safety of the transplantation process has been greatly improved and the success rate has steadily increased. For many patients, this therapy is no longer a distant "experimental technique" but a real and viable treatment option.
concluding remarks
From leukemia to autoimmune diseases, the scope of stem cell transplantation is expanding. It is not only a means of "curing" diseases, but also represents an important step in the direction of "repair and reconstruction". Although transplantation still involves certain risks, under strict evaluation and standardized operation, it has brought new hope to countless seriously ill patients.
In the future, with the optimization of transplantation techniques and the deepening of stem cell research, this therapy may continue to broaden the boundaries and become a key breakthrough for more difficult diseases.
Disclaimer: This article is intended only to disseminate scientific knowledge and share industry perspectives, and does not constitute any clinical diagnostic advice! The information published by Hangi Stem Cells is not a substitute for the professional advice of a physician or pharmacist. If you have any questions about copyright or other issues, please feel free to contact me.
郑重声明:本文版权归原作者所有,转载文章仅为传播更多信息之目的,如作者信息标记有错误,请第一时间联系我们修改或删除,多谢。

Leave a Reply